stone is how much harder than wood hardness test|unknown hardness scale : agent The Mohs Hardness Scale is a widely recognized and simple scale for measuring the scratch resistance of various minerals. Created by Friedrich Mohs, a German geologist, in 1812, it remains a standard in geology, . Comunicação - Soy Luna - Tu Historia para Android - Baixe .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Play Bejeweled online for free. Bejeweled is a popular game series that was first released by EA and PopCap Games in 2001. Originally created for gameplay on computers, the franchise has evolved over the years so that users can enjoy the game on their smartphones as well. As of 2021, the .
The Mohs Hardness Scale is a widely recognized and simple scale for measuring the scratch resistance of various minerals. Created by Friedrich Mohs, a German geologist, in 1812, it remains a standard in geology, . The Mohs hardness scale measures a mineral's resistance to .
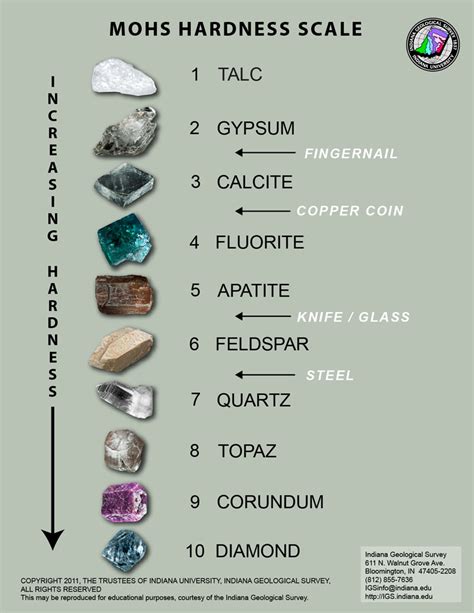
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material. The scale was introduced in 1812 by the German geologist and mineralogist Friedrich Mohs, in his book Versuch einer Elementar-Methode zur naturhistori.The hardness test developed by Friedrich Mohs was the first known test to assess resistance of a material to scratching. It is a very simple but inexact comparative test. Perhaps its simplicity has enabled it to become the most .This scale is a chart of relative hardness of the various minerals (1 - softest to 10 - hardest). Since hardness depends upon the crystallographic direction (ultimately on the strength of the .
When we measure the hardness of a mineral or natural stone, what we’re really measuring is its relative resistance to scratching. This is typically done by scratching one material against another of known hardness. In this . The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is an ordinal scale that tests the hardness of minerals based on their ability to scratch softer materials. The Mohs scale runs from 1 (softest) to 10 (hardest). Talc has a Mohs hardness of .Aug. Introduction to Mohs Hardness Scale: Understanding Mineral Scratch Tests. Delving into the world of geology, there’s a fascinating tool that has held the test of time in evaluating the hardness of minerals. Welcome to the realm .
The Mohs hardness scale is a qualitative test that measures the hardness of a mineral by its ability to visibly scratch softer minerals. The scale isn’t perfect, but it’s a great tool for quick identification of rocks in the field. Mohs Hardness Scale or Test tells you more about minerals and other material’s hardness based on which scratches the other or scratchability. So, the characteristic or property it tests is hardness. By modifying a process to test the hardness of metals, Janka invented the scale we still use today. The higher the number, the more durable the material. . And with a Janka rating of 5,060 lbf, it’s harder than stone. A .
The Janka hardness test is a variation or adaptation of the Brinell hardness test. The Janka scale ranges from 0 to over 4000lbf, with softer woods scoring lower on the scale and harder wood scoring higher. Some woods, .

unknown scratch hardness
In fact, much harder than nails, which typically have a Mohs hardness of about 6.5 (see our cross-referenced hardness charts for gemstones and other common materials above). . Peanut Wood Hardness. 6.5 - 7. Pearl Hardness. 2.5 - .The most common test for testing wood hardness is known as the Janka hardness test. The actual number listed in the wood profile is the amount of pounds-force (lb f) or newtons (N) required to imbed a .444″ (11.28 mm) . the dwarf ipe is much harder than Lignum Vitae Not all stone countertops are equal when it comes to hardness. Find out where many top countertop options rank on the Mohs Scale of Hardness. Call now for assistance: 201-440-6779. Visit our 360 Virtual Yard. . there are still many great options for hard stone countertops. Different stones are made up of different minerals, which impacts .Wood with a Janka hardness rating between 1,000 lb f. and 1,500 lb f. should be a suitable choice. By choosing wood within this hardness range, you would get an adequately hard type of wood to withstand scratches and dents. You could also work on the wood better. The harder the wood, the more difficult it is to work with.
There are alternative to both the Mohs scale and the Mohs test. Other scales include the Vickers, Brinell, Rockwell, and Rosiwall scales. Other tests include in the Knoop hardness test and Meyer hardness test. References. Mohs, Friedrich (1825) [Original German publication in 1822]. Treatise on Mineralogy: Or, The Natural History of the Mineral . The hardness of a wood is determined by the amount of force required to embed a 0.444-inch steel ball halfway into the wood’s surface. This test is known as the Janka hardness test and is widely used in the industry. The higher the Janka value, the harder the wood. The scale ranges from 0 lbf to over 5000 lbf, typically with exotic woods .
Flooring prices are dictated by how readily available the species of wood is, rather than how hard it is. Where The Wood Hardness Scale Comes From. The scale was developed as a means for displaying the results of the Janka hardness test. The test uses a 2″ x 2″ x 6″ piece of wood and a 0.444″ steel ball to determine how hard the wood is.
Understanding the durability ratings of hardwood is crucial when making your selection.One key factor to consider is the Janka hardness rating, which measures a wood species’ resistance to wear and denting.The higher the rating, the more durable the wood is. It’s also important to consider the finish of the hardwood, as well as the wood species itself, as . Steps for Performing the Mohs Hardness Test . Find a clean surface on the specimen to be tested. Try to scratch this surface with the point of an object of known hardness, by pressing it firmly into and across your test specimen.For example, you could try to scratch the surface with the point on a crystal of quartz (hardness of 9), the tip of a steel file (hardness . You’re building a deck and need to choose the right wood, or maybe you’re just curious about the science behind how hard different types of wood are. No matter your reason, you’ve come to . For perspective, sapphire hardness ranks at 9, but sapphires are 2-times harder than topaz (8 on the Mohs hardness scale) and 4-times softer than diamond (10). Unique Hardness Levels The basic 1-10 Mohs hardness scale numbers don’t apply to all minerals, and there are some irregularities you may come across.
Uniformity of Hardness: The Janka Hardness Test is performed on a specific sample of wood, typically cut in a certain way and dried to a standard moisture content. However, hardness can vary within a single tree, let alone between different trees of the same species. The Janka Hardness test determines how much power is needed to embed a 0.444-inch steel ball halfway into a wooden board. By measuring this level of penetration, an accurate rating of the wood's hardness can be .The basic idea of hardness is that a harder stone will scratch a softer one, if a sharp point or an edge of the harder material is drawn across the softer one. . This might be compared with a piece of wood that shows a different . The Janka hardness scale is a rating system used to determine the relative hardness of different wood species. The scale was invented by Gabriel Janka, an Austrian wood researcher, in 1906, and it measures the .
Wood is commonly measured by a test known as the Janka Hardness Test. This involves pressing a steel ball into the wood and measuring how deeply the ball dents the wood. When measured by the Janka Hardness Test, some hardwoods are softer than some softwoods, and they may also be softer than bamboo. You will use the above scale just like the Mohs hardness test kit. For instance, a copper penny (H=3) cannot scratch a specimen, but a knife (H = 5.5) does; its hardness lies between 3 and 5, i.e., it’s harder than calcite but softer than orthoclase.
The Mechanics of the Janka Hardness Test; Understanding Wood Species and Their Janka Ratings. Comparing Common Wood Species; . Janka's measured in pounds-force (lbf), showcasing how much oomph it takes to lodge that steel ball into wood. Is a Hard Maple 1450 a good Janka rating while White Oak is close to it?The most commonly used test to assess the hardness of wood is the Janka hardness test, which measures the resistance of a sample of wood to denting and wear. Technically speaking, it measures the force required to embed a steel ball into a sample of wood, and the resulting rating places that wood species on a scale.The Rockwell hardness number is not the same as the calculated depth differential measurement. Softer metals allow for deeper penetration than harder metals, so the B – A value will always be higher on soft metal test subjects than hard metals. The Rockwell hardness scale number appears inverse to the depth differential calculation. The most common way to measure wood hardness is by seeing how much force it takes to make an indent. . what determines the Janka hardness rating. So, the harder the wood, the more force it takes .
Glass is typically harder than epoxy resin but is considerably more fragile. In contrast, epoxy resin provides the same glossy and crystal-clear appearance as glass but with greater durability. Resin's natural flexibility means it can better withstand impact and is more likely to bend than break, unlike glass which can shatter. The higher the Janka rating, the harder the wood. For example, Brazilian Walnut has a Janka rating of 3,684 lbf. This means it took 3,684 pounds of force to press the steel ball into the wood sample. Meanwhile, Eastern White Pine has a low Janka rating of 380 lbf. So you can deduce Brazilian Walnut is nearly 10 times harder than White Pine.
The Janka Hardness Scale is an international standard for measuring the hardness of wood. It measures how much force it takes to embed a .444-inch steel ball in wood under controlled laboratory conditions. . It is important to note that the Janka test measures only how hard the wood is at its surface. The so-called softer wood beneath the . Understanding the Janka Hardness Scale. The Janka hardness scale tests a wood’s resistance to denting, dings and wear. It measures the force needed to embed a steel ball with an 11.28 millimeter or 0.444 inch-diameter halfway into a wood sample.
unknown mineral hardness
Betting At Doncaster. If you wish to have a bet on your race day at Doncaster, there are many places you can take part. Whether that's at one of the tote shops across each of our enclosures, with the bookmakers in the betting ring at the trackside, or from a tableside representative if you're enjoying hospitality.
stone is how much harder than wood hardness test|unknown hardness scale